Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

If you've ever experienced a quick spike and subsequent crash after eating a sweet meal, you have a basic understanding of glucose spikes. However, the adverse effects of temporary spikes in blood sugar levels are small compared to the overall damage that chronic or sustained high blood glucose levels can cause. Hormonal balance and general health.
And, while we mostly hear about blood sugar control in relation to heart disease and diabetes, it can also seriously affect otherwise healthy people.
Perhaps your recent physical exam and blood work indicated that your heart and metabolism look great. Maybe you're experiencing some occasional or annoying mood swings, weight fluctuations, or fatigue without an obvious culprit.
Regardless of your health status, monitoring your blood sugar — and lowering blood glucose levels — is an important way to support health and hormonal balance. What causes high blood sugar, and are you wondering why they can be harmful? Here's what you need to know.
A glucose spike refers to the release of sugar into the bloodstream at higher than normal levels. The process involves two main players:
If large amounts of carbohydrates are broken down too quickly and broken down into glucose at once, blood sugar levels can rise.
“This typically occurs after a meal, especially when eating foods high in sugar and carbohydrates,” says the registered dietitian. Kimberly WymanMS, RDN.
Under normal circumstances, the post-meal (after-meal) rise in blood sugar is normal and temporary. Over time, however, chronically elevated blood sugar levels can cause serious disruption to our body's fundamental systems.
“It can cause a drop in blood sugar Insulin sensitivityIt can disrupt hormone balance, including estrogen,” he said. Nicole Levin, MDCalifornia-based physician.
Decreased insulin sensitivity causes the pancreas to produce more and more insulin to encourage resistant cells to take up glucose. If those cells don't respond appropriately—perhaps because they're already saturated with glucose—sugar can build up in the blood.
That stored glucose can be stored as fat, where small amounts of estrogen are produced. In this case, it can be more fat It disturbs the level of estrogen.
“Studies show Increased blood sugar, insulin resistance, alters estrogen metabolism and disrupts hormone balance, Levine says.
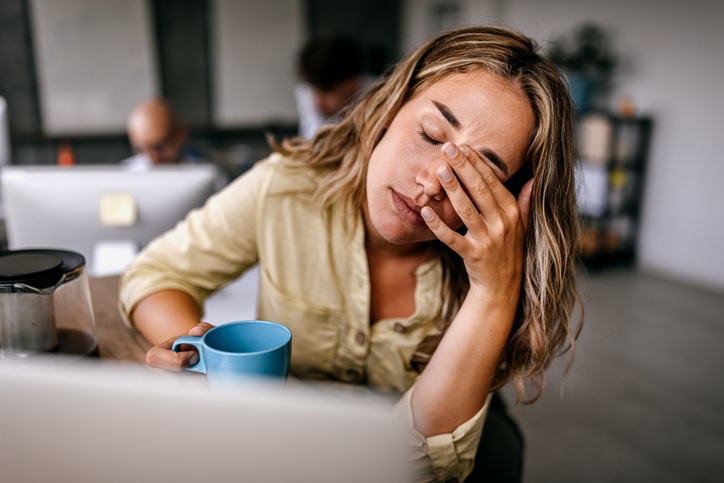

You experience the lows after a sugar rush. “Some common symptoms of high blood sugar are thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, headache, irritability, and extreme hunger,” says Levine.
Over time, however, chronic high blood sugar along with daily stress and lack of exercise can cause hormonal imbalance. This can lead to symptoms including:
If you believe you may be experiencing high blood sugar, ask a healthcare professional.
Normally, when carbohydrates enter the body, glucose levels temporarily increase (b One to two hours). Then food is converted into energy, and the blood sugar level returns to the original line.
“It's natural for blood sugar levels in the body to rise and fall throughout the day, and it's higher with each meal,” he says. Dr. Candice Sethi, Certified Personal Trainer and Clinical Psychologist specializing in eating disorders.
But some triggers can cause high blood sugar levels.

Think of how a log burns the way a match burns.
Consuming your carbs in simple form causes them to be digested quickly – for a short burst of energy – thus causing a faster (and sharper) rise in blood sugar.
“White rice, pasta, and Prepared foods Instead, they are more likely to cause high blood sugar. Healthy carbohydrates Like whole-grain breads and cereals,” Sethi says. Of course, candy, soda, and other sugary, high-Glycemic Treatments can also increase glucose levels.
However, more Complex and fibrous carbohydratesLike those in whole fruits, vegetables, and grains, they digest more slowly and sustainably. This lends them to a more gradual absorption and a post-meal insulin curve that is as opposed to steep.
In response to stress, the adrenal glands are released Cortisol. This hormone directs the body to release glucose stored in the liver so it has the energy to deal with a perceived threat, whether it's a charging lion or a looming deadline.
But the body does not distinguish between the two. So if you're in a constant state of stress, a constant stream of cortisol is released — and, by extension, blood sugar — in response.
And because excess glucose is often converted to fat – and some of the body's estrogen It is produced in fat tissue – High levels of stress can disrupt estrogen levels over time. High levels of estrogen can increase the level of cortisol in the blood, which triggers the stress response and further perpetuates the cycle.
Sleep duration, quality and consistency all have it. found to directly affect insulin sensitivity.
“A disruption in your sleep cycle can cause your body to use insulin more efficiently.
Although more research is needed, researchers have identified several contributors to decreased insulin sensitivity due to insufficient sleep. An increase in disease markers and biomarkers, disturbances in circadian rhythms, insufficient exposure to light and high cortisol levels were observed in the tests.
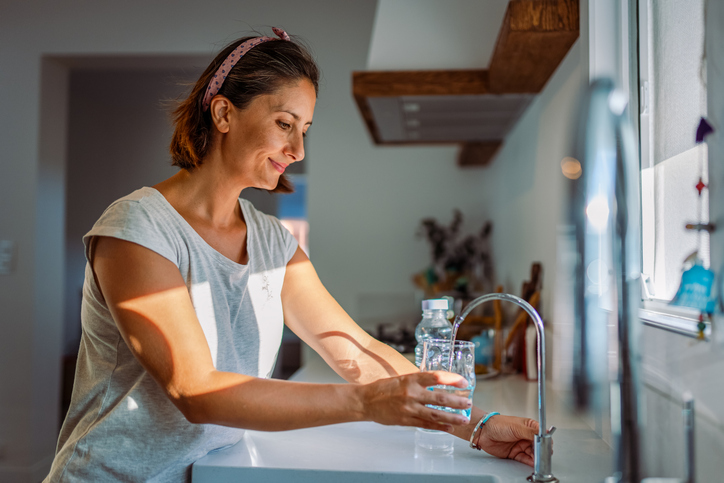

Your total blood volume consists of a large amount of water. If you don't drink enough, the amount of blood in the blood will decrease, which will make the proportion of glucose relatively high.
As a result, dehydration It can concentrate the glucose level in the blood. It may be. It affects hormones Affecting blood sugar levels.
Add to the list of reasons to feed yourself First thing in the morning Correct regulation of your blood sugar throughout the rest of the day.
“Waiting until noon to take the first bite can cause your blood sugar to spike After lunch and dinner” says Sethi.
Researchers are still hypothesizing as to why, however They got it Skipping breakfast makes the liver resistant to insulin and increases glucose levels. As a result, they observed that blood sugar levels were higher after lunch.
There are many lifestyle modifications you can make to help control glucose levels.
Of course, some symptoms are more severe than others. If you have any concerns about how your body handles blood sugar, you should consult a doctor.
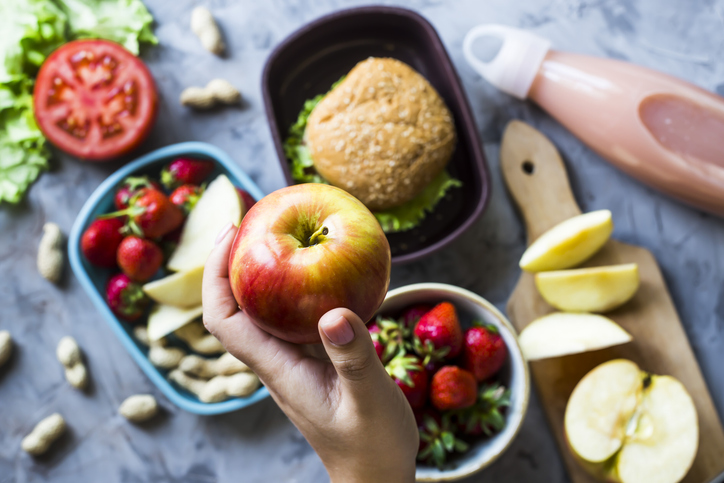

Keeping blood sugar levels at bay starts with eating a healthy, balanced diet. And that starts with Limiting added sugar And treat the types of carbohydrates you choose for energy.
keep in mind – Simple carbohydrates It can burn quickly and cause blood glucose to rise and fall. Complex carbohydrates And fiber digests more slowly, keeping post-workout blood sugar levels stable and providing a more consistent source of energy.
In combination Macros It also helps.
“When we consume carbohydrates, it's important to have a source of protein, fat, or fat. Fiber With it, “says Viman. This prevents blood sugar from rising by reducing the amount of sugar that enters the blood.
“You can prevent blood sugar spikes,” Levine agrees Stay hydrated and eating Balanced meals With fiber and protein.
Making exercise a part of your daily routine is key to helping lower blood sugar levels quickly and long-term.
Regular exercise helps stabilize blood glucose levels in general Improve insulin sensitivity” says Levine.
This is because the more demands you place on your body, the more receptive it is to the blood glucose needed to meet those demands. And the more muscle you build, the more tissue you have To absorb the amount of sugar circulating in the blood.
Additionally, exercising after eating can provide immediate benefits.
“Participating in some form of exercise shortly after a meal It helps to reduce the sugar level in the blood” says Wyman. “Exercise stimulates the body to pull sugar from the bloodstream into the muscles.”
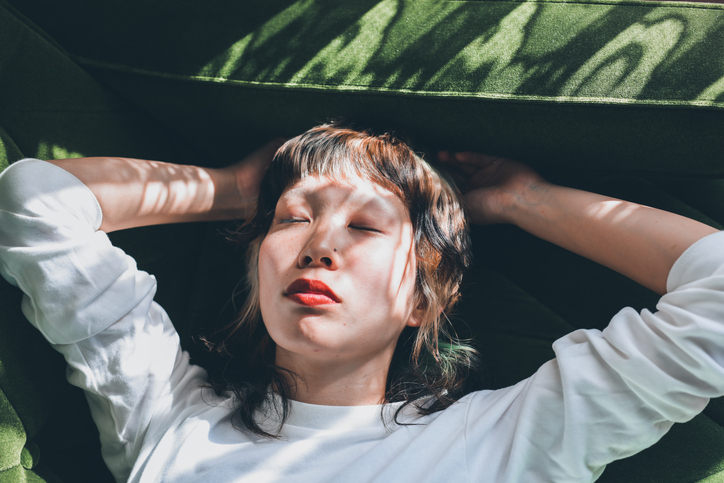

Researchers have found Sleep length, quality and time each have a significant impact on blood sugar, which already It arises naturally In the last hour of sleep – a physiological response known as the “morning phenomenon” – helps to wake up.
To make sure those nighttime struggles get off to a healthy start, Studies show Sleeping for seven consecutive hours is associated with greater insulin sensitivity.
This is not permission to sleep as a college freshman; to find Too many shutee It immediately puts you in danger. But increase About an hour Nighttime fasting can help improve blood glucose levels and control.
A number of vitamins, minerals, herbs and other nutrients have been found to help support normal blood sugar and reduce postprandial glucose spikes. Some see nutritional gaps, while others find it difficult to get enough from food alone.
Certain ingredients, such as Belle Vitale Daily Metabolism & Blood Sugar Support, help your body burn natural fat, support a healthy metabolism, and help maintain normal blood sugar levels:*
Other supplements may also help address the role of stress in having a positive effect on blood sugar:
These modifiers, combined with other essential vitamins and minerals found in Belle Vitale Daily Hormone & Stress Support, help combat the effects of stress, support healthy cortisol levels, and promote healthy hormones.*
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.